In this installment in our series about how Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) are affecting whole industries, we look at agriculture to find out that AVs drive higher efficiency, but are also a lever for wider use of technology, enabling increased productivity and sustainability.
As global food demand rises, labor shortages persist and factors such as climate change and geopolitical conflicts threaten production, innovative technologies are stepping in to help farmers meet these challenges head-on. In 2024, the agricultural sector is witnessing a significant shift towards automation, with autonomous vehicles leading the charge in transforming traditional farming practices.
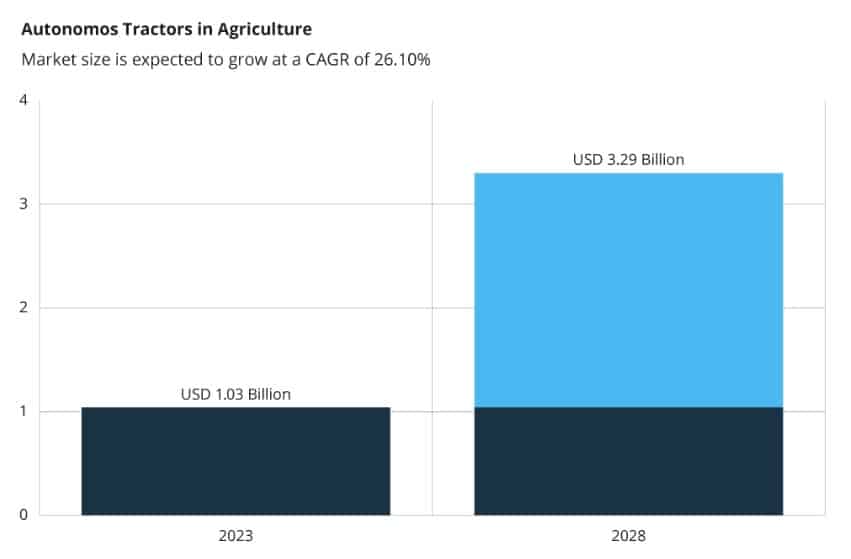
Source: Infopulse
The Role of Autonomous Vehicles in Modern Farming
Autonomous vehicles in agriculture encompass a wide range of machines, from self-driving or remotely-driven tractors to robotic harvesters. These systems rely on advanced technologies such as GPS, AI, computer vision, and sophisticated sensor arrays to navigate fields and perform tasks without a human on board. AVs often integrate with and feed into additional precision agriculture technologies, including sensors, sprayers or robotic tools.
Here are some of the key benefits of autonomous trucks and tractors:
Efficiency and Productivity
Autonomous tractors are transforming the agricultural landscape by dramatically increasing farm productivity and efficiency. These tireless machines can operate around the clock without breaks, completing farming tasks faster and more precisely than their human-operated counterparts. The ability to coordinate multiple autonomous tractors simultaneously further amplifies this efficiency boost. This increased productivity is coupled with reduced operational costs, as autonomous tractors eliminate the need for human operators, consume less fuel due to optimized pacing, and require less maintenance owing to their smoother operation.
Aswin Dierx, a crop worker at the National Fieldlab for Precision Farming (NPPL) in the Netherlands highlights autonomous tractors’ fuel efficiency. “Unlike a human driver, the tractor doesn’t press the gas pedal to finish faster,” Dierx noted. “An extra hour of work is no problem.”
Addressing Labor Challenges and Enhancing Safety
Agriculture, like many other “Dull, Dangerous, Dirty” jobs, is facing a severe labor shortage. By taking over routine and labor-intensive tasks, these machines allow farmers to allocate human resources more strategically. Moreover, the use of autonomous tractors significantly improves farm safety. By removing human operators from potentially dangerous situations and minimizing exposure to hazardous chemicals and pesticides, the risk of accidents and injuries on the farm is greatly reduced. This not only protects the workforce but also potentially reduces insurance costs and liability for farm owners.
Precision Agriculture and Environmental Stewardship
One of the most significant advantages of autonomous tractors lies in their ability to enhance precision and accuracy in farming operations. Equipped with advanced GPS, sensors, robotic tools and AI technologies, these machines excel at precise application of inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides. This precision not only reduces waste but also leads to improved crop yields. The environmental benefits are substantial, with optimized resource use promoting more sustainable farming practices. Reduced chemical usage and minimal soil compaction, especially from lightweight electric models, further contribute to environmental conservation. This level of precision enables farmers to practice data-driven agriculture, making informed decisions based on real-time data collection and analysis.
Scalability, Flexibility, and Future-Proofing Farms
The scalability and flexibility offered by autonomous tractors are invaluable in modern farming. Operations can be easily scaled up by adding more autonomous units as needed, without the complexities of hiring and training additional staff. These machines can be customized and adapted to specific crops or terrains, providing versatility across different farming contexts. Furthermore, the adoption of autonomous tractors positions farms at the forefront of agricultural technology, preparing them for future advancements in the field. By embracing this technology, farmers are investing in a more sustainable and efficient future for their operations, capable of meeting the increasing demands of modern agriculture while potentially improving their profitability.
Use Cases and Examples of Autonomous Vehicles in Agriculture
Automated Tractors and Plows
John Deere, a pioneer in agricultural automation, has made significant strides in 2024 with its autonomous tractor technology. The company’s latest models, equipped with advanced AI and machine learning capabilities, have been widely deployed across North America and Europe.
A 10,000-acre farm in Illinois, U.S., reported a 15% increase in productivity using John Deere’s latest autonomous tractors. The farm credited precision planting, optimized tilling, and reduced overlap in field operations as key factors driving their improved efficiency.
Autonomous Vineyard and Orchard Management
Bluewhite Robotics has made significant inroads with its autonomous systems for orchards and vineyards. Their innovative approach involves retrofitting existing tractors with autonomous capabilities, enabling tasks such as pruning, spraying, and mowing to be performed without direct human control.
The impact of this technology is evident in California’s Napa Valley, where vineyards using Bluewhite Robotics’ systems achieved ROI in one year. Moreover, these vineyards have achieved more consistent grape quality through precision spraying, demonstrating how autonomous technology can enhance both efficiency and product quality in specialized agricultural settings.
Bluewhite technology has proven to reduce operational costs in different use cases by up to 85%.
Autonomous Soil Analysis and Seeding
Precision agriculture has taken a leap forward with companies like Small Robot Company developing autonomous vehicles for soil monitoring and seeding. These systems use advanced sensors and AI to map soil health, optimize seeding depth, and manage nutrient application with unprecedented accuracy.
Additional Benefits from Autonomy
The efficiency gained through autonomous tractors’ 24/7 operation can be leveraged to reduce the size of machinery. In agriculture, this is a critical consideration as smaller tractor form factors allow for better maneuverability which enables greater precision – which improves yield. The smaller vehicles form factor also reduces soil compaction and fuel consumption.
The “Hands Free Farm” – a multi-year experiment by Harper Adams University suggest a production cost saving of £20 to £30 per tonne when producing wheat using autonomous tractors.
Conclusion
The adoption of autonomous vehicles in agriculture is rapidly transforming the industry, offering solutions to pressing challenges such as labor shortages, efficiency demands, and environmental concerns. The varying ways that AV are used in different applications and use cases in the agriculture industry shows that while young, these technologies are not just theoretical concepts but practical tools delivering tangible benefits to farmers.
As we look to the future, the continued development and adoption of autonomous vehicles across industries, we see how they drive resilient and sustainable practices.






